Next.js 15 was released earlier today and I’m thrilled to share my recent journey upgrading a key project from Next.js 14 to Next.js 15. This adventure was undertaken to test out the latest features and understand the upgrade experience from a firsthand perspective—essentially stepping into the shoes of the broader user community.
Why Upgrade to Next.js 15?
The motivation to upgrade wasn’t driven by a pressing need but rather by an eagerness to explore new enhancements. Key features like the improved Turbopack and the default no-cache option particularly caught my eye. My goal was to see how seamless (or challenging) the upgrade process would be for real-world applications.
Setting the Expectations and Preparing for the Journey
Expectations:
Seamless Codegen: I hoped the codegen tool would manage most of the heavy lifting.
Manual Interventions: Knowing the complexity of my monorepo, I prepared myself for some manual fixes.
Preparations:
Documentation: I dived deep into the official Next.js 15 docs as well as the Upgrade Guide
Videos: Followed insightful videos by LeeRob on Next.js 15 RC2.
Starting the Upgrade Process
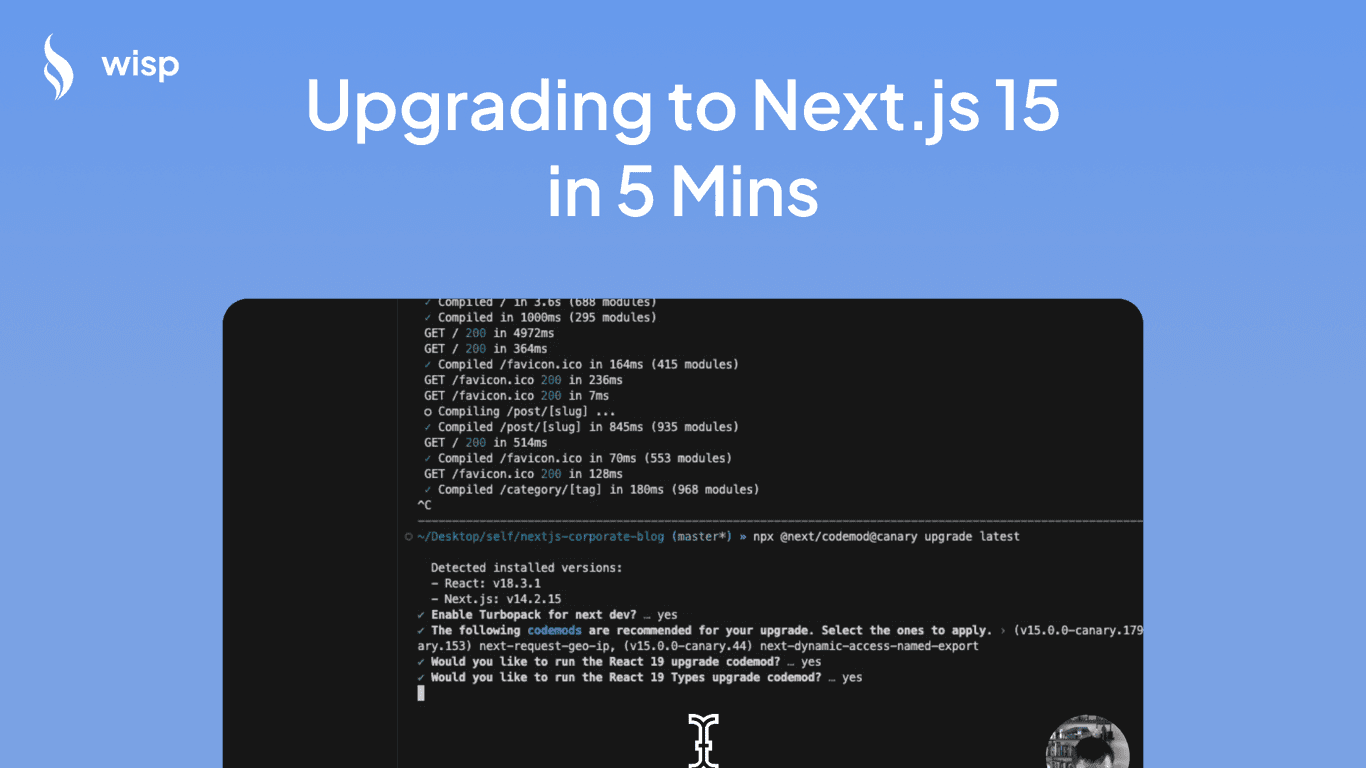
With a mix of excitement and trepidation, I initiated the upgrade using the npx @next/codemod@canary upgrade latest command. Initially, the codegen tool performed admirably, handling a bulk of the transformations effortlessly. But as the build process continued, multiple failures emerged, and my optimism began to wane.
Facing Codegen Challenges
Despite its initial success, the codegen tool encountered hitches with certain synchronous to asynchronous API transitions, necessitating manual tweaks.
Layout Props: The automated codemod didn’t fully address synchronous layout props transitioning to asynchronous.
Before:
export default async function Layout(props: PropsWithChildren<{ params: { path: string | string[] } }>) {
const { path } = params;
const { children } = props;
}After:
export default async function Layout(props: PropsWithChildren<{ params: Promise<{ path: string | string[] }> }>) {
const params = await props.params;
const { path } = params;
const { children } = props;
}Cookies Function: Transitioning from synchronous to asynchronous cookies functions was another hurdle.
Before:
const sessionId = cookies().get(lucia.sessionCookieName)?.value ?? null;After:
const sessionId = (await cookies()).get(lucia.sessionCookieName)?.value ?? null;Tackling React 19 Compatibility
Upgrading to React 19 introduced its own set of challenges, with significant changes in ReactNode and other internals.
Issue: Incompatibility with React 19.
Solution: Upgraded to
framer-motion@12.0.0-alpha.1.Details: Check out GitHub Issue #2668.
Issue: Outdated
@react-email/componentscausing type errors.Solution: Upgraded using the command
pnpm up @react-email/components@latest.Details: See GitHub Issue #1413.
Issue: Broken types due to non-matching peer dependencies.
Solution: Temporarily used
anyto bypass type errors while waiting for it to be patched for React 19.
Change: Explicit initialization needed.
Before:
const ref = useRef<number>(null);After:
const ref = useRef<number | null>(null);
Common Errors and Their Resolutions
Error: TypeError: Cannot Read Properties of Undefined (ReactCurrentDispatcher)
Solution: Ensured matching versions of
reactandreact-dom.More Info: Refer to the Stack Overflow Discussion.
Grappling with Turbopack Limitations and Monorepo Challenges
Turbopack, while powerful, currently doesn’t support externals like Webpack. This necessitated removing --turbo from the build commands and reverting to Webpack.
Handling the monorepo configuration posed its own set of challenges. Ensuring compatibility across numerous sub-repositories, combined with legacy boilerplate code, certainly tested my patience.
Strategy: Moved the pnpm override to the root directory to maintain consistency across the entire monorepo.
Recommendations for Smoother Upgrades
To navigate the upgrade terrain more efficiently, here are a few steps I found helpful:
Incremental Upgrades:
Tackle one component at a time to better isolate and address issues.
Manual Downgrade:
If overwhelmed by issues, upgrade Next.js to 15 first while initially downgrading
reactandreact-domto version 18.x.x. Once stable, proceed with upgrading React.
Conclusion
Upgrading to Next.js 15, especially alongside React 19, is indeed a complex venture filled with numerous challenges. However, through careful planning, utilizing community resources, and adopting an incremental upgrade approach, the process is manageable. Staying in tune with the latest from Next.js and React will further ensure smoother transitions in the future.
For more detailed insights, refer to the official Next.js 15 Upgrade Guide.